Ternary Operator in C
Ternary Operator in C
If any operator is used on three operands or variable is known as Ternary Operator. It can be represented with ? : . It is also called as conditional operator
It helps to think of the ternary operator as a shorthand way or writing an if-else statement. Programmers use the ternary operator for decision making in place of longer if and else conditional statements.
The ternary operator is an operator that takes three arguments. The first argument is a comparison argument, the second is the result upon a true comparison, and the third is the result upon a false comparison. Ternary operator is shortened way of writing an if-else statement.
Ternary operator is a?b:c it say that the condition a is true b will be executed else c will be executed.

Advantage of Ternary Operator
Using ?: reduce the number of line codes and improve the performance of application.
Syntax
expression-1 ? expression-2 : expression-3
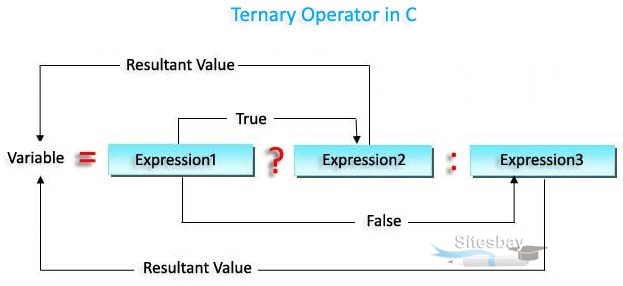
In the above symbol expression-1 is condition and expression-2 and expression-3 will be either value or variable or statement or any mathematical expression. If condition will be true expression-2 will be execute otherwise expression-3 will be executed.
Syntax
a<b ? printf("a is less") : printf("a is greater");
Flow Diagram
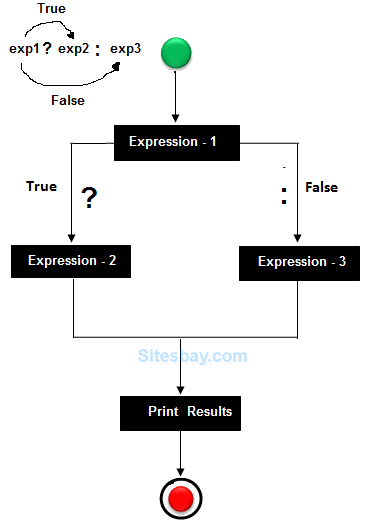
Find largest number among 3 numbers using ternary operator
Find Largest Number among 3 Number in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a, b, c, large;
clrscr();
printf("Enter any three number: ");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
large=a>b ? (a>c?a:c) : (b>c?b:c);
printf("Largest Number is: %d",large);
getch();
}
Output
Enter any three number: 5 7 2 Largest number is 7
Example for Ternary Operator in C
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=2,b=4,c=9;
int lar;
lar=(((a>b)&&(a>c))?a:((b>c)?b:c));
printf(“Largest Number is: %d”,lar);
return 0;
}
Output
Largest Number is: 9

